ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
NEC Trains Robotics AI to Handle Unorganized Items
NEC Corporation has developed an artificial intelligence (AI) technology for robotics that enables precise handling of unorganized and disorderly placed items. Specifically, the new technology predicts both the areas hidden by obstacles and the result of a robot’s actions. Thus, it enables robots to perform tasks that were previously performed manually. Generally, it contributes to the improvement of productivity and work-styles.
Background
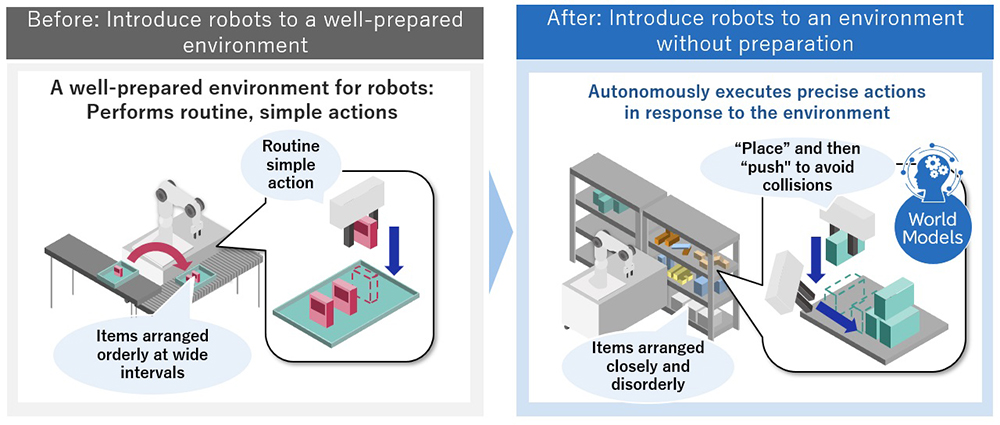
Recently, due to labor shortages and other factors, the need for automation through the introduction of robots and large-scale equipment has been increasing in logistics warehouses and factories. However, it is difficult for existing robotics technologies to correctly recognize an environment in which objects and obstacles are disorderly placed. Thus, preparing an environment is necessary so that a robot can easily perform its tasks. For this reason, the introduction of robots has been limited to simple, routine tasks.
Features of this Technology
This time, NEC has developed an AI technology for robotics that consists of two technologies: “World Models” (*) – “Spatiotemporal Prediction,” in which a robot precisely predicts the work environment and the results of its own actions from camera data, and “Robot Motion Generation,” which automatically generates optimal and precise actions based on these predictions. According to NEC research, this is the first technology of its kind to be applied to robot operations.
1. Autonomously executes precise actions in optimal sequences for items of various shapes and sizes
The handling of objects performed manually at a work site are executed by a combination of various actions. For example, in packing items, people can instantly execute a combination of precise actions such as “placing and then pushing items” without hitting other objects or obstacles.
In robot control that uses conventional technologies, however, actions such as “push” and “pull” are more difficult to execute with high precision than actions such as “pick up” and “place.” This is because slight differences in actions or shapes significantly influence how objects move in response to actions. In addition, the number and types of actions to be considered increase. Thus, the combination and sequence of actions becomes more complex, which makes real-time planning a challenge.
This technology uses World Models to accurately predict the results of robot actions on objects of various shapes from video camera data. Thus, it enables robots to execute precise actions such as “push” and “pull.” Moreover, robots can autonomously and instantly execute combinations of multiple actions such as “place and push” and “pull and pick up” by generating the appropriate action sequence at real-time speed depending on the work environment.
2. Operates while predicting hidden and invisible items
In a work environment where multiple items are closely arranged or disorderly piled up, people naturally predict the hidden areas and act accordingly; for example, picking up items while avoiding interference with hidden objects. However, conventional recognition technology for robots has been difficult for practical use. Mainly, it requires the preparation and learning of a large amount of teaching data showing the state of hidden objects to predict the hidden areas.
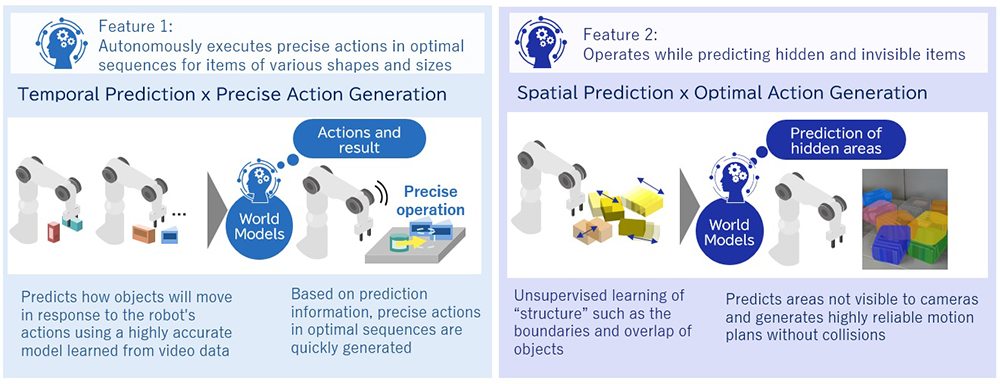
This new technology enables unsupervised learning that does not require labeling through the application of World Models. Also, it can efficiently learn prediction models of hidden object shapes. This allows robots to accurately predict a work environment from camera data and automatically generate optimal actions that do not collide with other objects or obstacles.
Future Development
By the end of 2024, NEC will test this technology in logistics warehouses and other sites where much of the work is done manually. It will promote social implementation of this technology in various industries with significant need for automation. Thus, NEC aims to contribute to improved productivity and work style reform.
(*) Technology that enables a robot to predict what will happen in the real world as a result of a certain action without trying it out in reality. This has been attracting attention in recent years as a key technology for autonomous control.




