ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
New Proterial Magnetic Shielding Sheet Suits xEVs
Proterial, Ltd. has developed the MS-FH highly heat-resistant magnetic shielding sheet. It highlights an improved heat resistance over the MS-F magnetic shielding sheet made of nanocrystalline soft magnetic material FINEMET®. Specifically, MS-FH has improved heat resistance up to 130°C – 50°C higher than the previous product – and features approximately 40% thickness. As a result, MS-FH contributes to the miniaturization and weight reduction of electronic devices.

Product Background
The MS-F magnetic shielding sheet made of FINEMET provides excellent magnetic properties including high magnetic permeability*1 and saturated magnetic flux density*2. Additionally, it is thin, lightweight, flexible in its handling, and provides good processability for easy cutting, punching, etc. It has been used for noise suppression in a wide range of applications. Among them are electronic devices including mobile phones, PCs, cameras, in medical equipment such as X-ray diagnostic equipment. Also, it is employed in shielded rooms designed to reduce geomagnetism and other external magnetic fields.
In recent years, MS-F has increasingly been used in noise suppression applications for in-vehicle electronic equipment on xEVs*3. However, sheets with heat resistance greater than MS-F were needed as its usable temperature was 80°C or lower. This means that high-temperature conditions on vehicles would cause the protective film and adhesive to deteriorate, thus affecting its magnetic properties.
Overview of MS-FH Magnetic Shielding Sheet
Through further research into MS-F’s protective film, adhesive material, and manufacturing conditions, Proterial has successfully developed MS-FH, a new magnetic shielding sheet with a heat resistance of 130°C. The structure features integrated FINEMET and protective films thus laminate molding (see illustration).
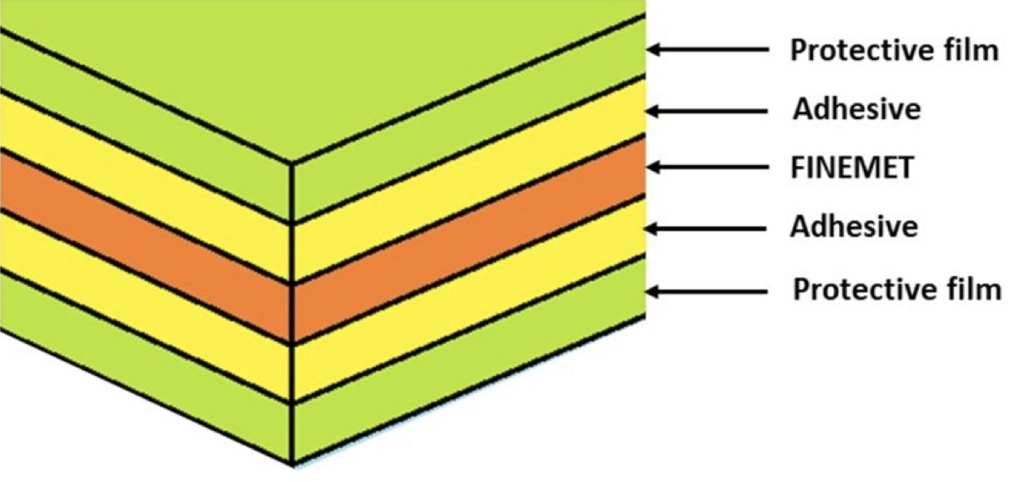
Generally, the peeling of protective films causes heat resistance issues in the previous MS-F sheets. This is due to the adhesive re-melting under high temperatures, as well as cracks, dropouts, etc. Specifically, they occur in FINEMET due to protective films shrinking as caused by their low heat resistance, resulting in deterioration of magnetic properties. Through further research into protective films, adhesive materials, and manufacturing conditions, these issues have been addressed in MS-FH, resulting in improved heat resistance.
In making improvements to protective films, Proterial considered not only whether the protective films would remain stable at high temperatures, but also their physical properties. Thus, it chose materials that would not deteriorate FINEMET’s magnetic properties. Furthermore, manufacturing processes that may potentially affect the properties of FINEMET—especially conditions in lamination processes where thermal expansion and contraction occur due to heating—were revised. This also contributed to achieving the magnetic shielding sheet’s high heat resistance.
Mainly, MS-FH exhibited excellent heat resistance properties as evidenced by showing no deterioration to its protective film or adhesive. Also, no significant change happened to its magnetic properties after undergoing high temperature tests run at 130°C for 1,000 hours. Thus, it suits noise suppression applications at high temperatures where the previous MS-F magnetic shielding sheet could not. Resin materials and adhesives used in MS-FH are UL94 VTM 0*4 certified for high flame retardancy.
Furthermore, thanks to the protective films and adhesive layers being thinner than those in the company’s previous product, MS-FH is only 0.05mm thick. As a result, it is approximately 40% of the thickness and weight of its previous product, which was 0.13mm thick. In achieving this, manufacturing problems that can occur with thinner protective films and adhesives were avoided by revising processing conditions. Also, because of the deterioration of its protective functions, reliability tests were conducted to verify that there were no problems.
In addition to its improved heat resistance up to 130°C, 50°C higher than the previous product, its thinner profile means that MS-FH can be used in high-temperature environments such as automotive applications and in narrow spaces that previously posed difficulties and in applications expected to diversify going forward, contributing to the miniaturization and weight reduction of electronic devices and other equipment.
Production Status -40~+80°C
Availability of samples started Dec. 2023. Meanwhile, mass production is on Dec. 2024.
Notes:
*1: Magnetic permeability: This value indicates the ease at which magnetism can pass through a material.
*2: Saturated magnetic flux density: Magnetic flux refers to the flow of magnetism per unit area and represents the strength of a magnet. While magnetic flux density will increase when an external magnetic field is applied to a magnetic material, there is a limit to flux density beyond which it will not increase any further. The higher this value, the stronger the magnet.
*3: xEV is a generic term that refers to electric vehicles. It covers BEV (Battery Electric Vehicle), HEV (Hybrid Electric Vehicle), PHEV/PHV (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle/Plug-in Hybrid Vehicle), FCEV/FCV (Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle/Fuel Cell Vehicle), etc.
*4: UL94 VTM-0: The most demanding rating under UL94, a standard established by Underwriters Laboratories Inc. (UL) to certify the flame retardancy of materials.
FINEMET is a registered trademark of Proterial, Ltd.




