ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
Sumitomo Bakelite's New Sheet for Power Modules
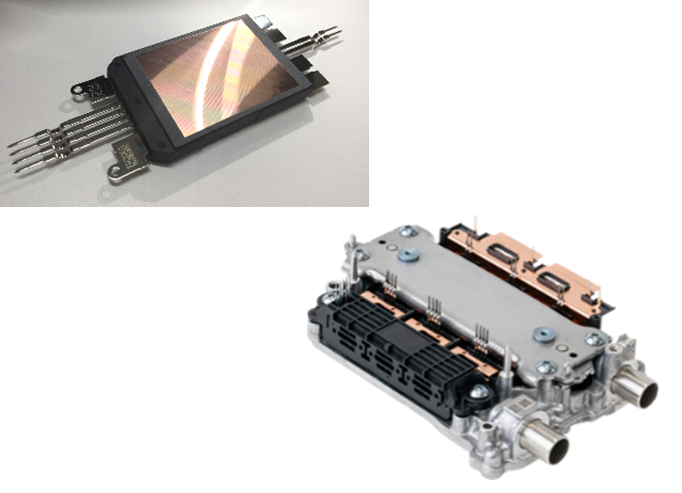
Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd. has developed a heat-dissipating insulating sheet that combines industry-leading thermal conductivity with electrical insulation properties. Accordingly, the product enables the replacement of conventional ceramic substrates used in power modules. At the same time, it has been adopted as the insulating layer of resin-insulated substrates manufactured by NHK Spring Co., Ltd., which are used in power modules within automotive inverters produced by DENSO Corporation.
Background of Development
Power modules are critical devices that play a central role in power conversion and control systems, and they are widely utilized across various fields, including industrial equipment, the automotive sector, renewable energy, and consumer applications.
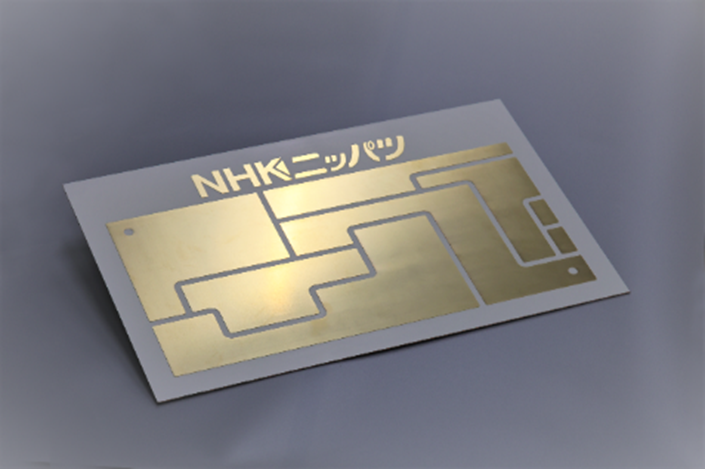
* The image shown is for illustrative purposes only
and differs from the actual mass-produced product. Image provided by: NHK Spring Co., Ltd.
In recent years, the adoption of SiC power semiconductors has driven further advancements in performance. Particularly, in the automotive industry, power modules are extensively used in EV and PHEV inverters, DC-DC converters, and other applications, contributing to extended vehicle range, improved energy efficiency, and reductions in CO2 emissions.
As the evolution of electric vehicles (EVs) progresses, there is an increasing demand for power modules capable of handling higher currents and voltages, along with the need to address the heat generated. Since 2018, Sumitomo Bakelite been fully engaged in the development of heat-dissipating insulating sheets designed to meet the stringent requirements for high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation in power module components, and we have been advancing mass production.
About BLA-6051 Heat-Dissipating Insulating Sheet
This product is a thermosetting resin adhesive sheet with high thermal conductivity and high electrical insulation. It enables the replacement of ceramic substrates when used as the insulating layer of resin-insulated substrates. By developing a proprietary high-thermal-conductivity resin and incorporating it into the heat-dissipating insulating sheet, we have achieved the following five key features:

Industry-Leading Thermal Conductivity
By utilizing advanced heat-dissipating resin and BN filler orientation control technology, we have achieved thermal resistance comparable to silicon nitride (AMB substrates) in resin-insulated substrates. This exceptional heat dissipation capability enhances thermal management performance in electronic and industrial equipment, suppressing temperature increases and significantly improving product reliability.
High Voltage Resistance
The sheet offers excellent electrical insulation, essential for electronic equipment, ensuring safety and reliability even in high-voltage environments.
Thin Film Capability
By leveraging the characteristics of resin materials, this product enables thin-film applications. It contributes to weight reduction and enhances design flexibility, thereby expanding its applicability to a wide range of next-generation products.
Dimensional Stability with Minimal Warpage
The sheet provides excellent heat resistance, capable of withstanding continuous operation at temperatures above 150°C. Compared to ceramic substrates, it exhibits superior performance in reducing warpage during semiconductor chip mounting and in power module products. This enhances design flexibility, simplifies the assembly process, and improves yield by minimizing warpage-related issues.
Replacement of Ceramic Substrates
Replacing ceramic substrates with resin-insulated substrates is expected to reduce costs. Additionally, leveraging the unique strengths of resin materials allows for the addition of enhanced properties, achieving both cost reduction and high performance. This approach effectively resolves the challenges previously associated with ceramic substrates.
20 January 2026




