ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
Molex’s Survey Shows Steady Growth of Industry 4.0
Molex has announced the results of a global survey of Industry 4.0 manufacturing stakeholders in robotics, complex machines, and device or control systems. The findings reflect steady progress in the development of Industry 4.0 initiatives across the industrial automation ecosystem, including smart automation, connectivity, and analytics that add efficiency and intelligence throughout the manufacturing lifecycle.
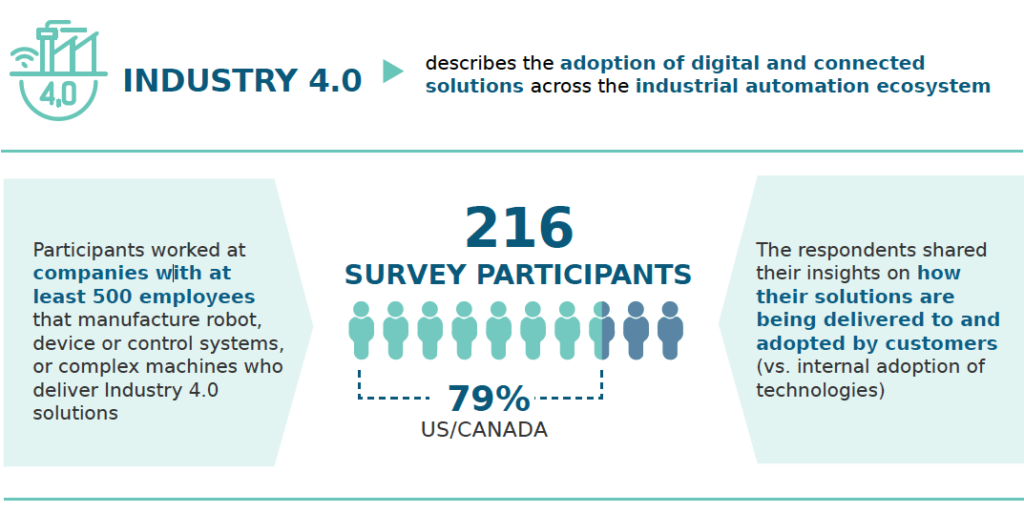
Dimensional Research was commissioned to conduct The State of Industry 4.0 Survey last June, polling 216 qualified participants in a variety of roles, such as R&D, engineering, production manufacturing, strategy, innovation, and supply chain management. The primary research goal was to capture data on practical Industry 4.0 experiences and opinions. Overall, the survey respondents validated continued growth, potential customer benefits and expected business outcomes emerging from the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and smart manufacturing.
Based on the survey, 51 percent of respondents have a well-defined Industry 4.0 corporate priority with executive sponsorship; 49 percent have already achieved success while 21 percent are still in the investment stage. Also, more than half of the respondents expect to meet their Industry 4.0 goals within two years, while a third believe it will take three to five years to reach that milestone. Among them, 58 percent say that digital transformation investments have accelerated Industry 4.0 efforts, while 44 percent find organizational and cultural adoption barriers hardest to overcome.
Survey Details
The most impactful business outcomes encompass the ability to build better products (69%), reduce overall manufacturing costs (58%), increase revenues (53%), offer products at lower prices (35%) and decrease time-to-market of new solutions (35%). For machine builders, robot manufacturers and systems integrators, the opportunity to expand factory-floor automation and intelligence is expected to drive significant customer gains.
Among the most anticipated customer benefits are increased efficiency of robots, machines, and other manufacturing assets (58%); greater flexibility on manufacturing lines (50%); the use of advanced analytics or Digital Twins to self-optimize operations (50%); virtual design and simulation of new production facilities before making capital expenditures (42%); elevated labor productivity (41%); and unlocked access to real-time data across facilities (26%).
Among the capabilities considered most beneficial to their organizations’ Industry 4.0 efforts, respondents cited machines embedded with ample intelligence to control their own processes while interacting externally (53%).
Despite overwhelming optimism for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, persistent cultural, business model and technology challenges thwart implementation. Nearly half of those polled identified problems with leadership that doesn’t advocate for change, making it more difficult to reap full value from investments.
Most of the respondents also face major business model challenges, spurred by a range of complex and costly requirements, such as difficult funding decisions (45%), upfront investments that complicate ROI (42%) and lack of clarity on which use cases pose the greatest payoffs (40%). A litany of technology hurdles exist topped by separate IT and OT network infrastructures (43%), restrictive communications protocols (39%), and limited remote access (36%).