ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
Toyota, Idemitsu Partner on EV Battery Mass Production
Idemitsu Kosan Co.,Ltd. and Toyota Motor Corporation have agreed to work together in
the mass production of all-solid-state batteries for battery electric vehicles (BEVs). Particularly, the two companies will develop solid electrolyte technologies, as well as improve productivity and establish a supply chain.
Through this collaboration, the two companies seek to ensure the successful commercialization of all-solid-state batteries between 2027 to 2028. The two companies have been leading in their respective fields, including material development relating to all-solid-state batteries.

The cooperation is a major step in the respective company’s approach to achieving carbon neutrality. Primarily, Idemitsu has been working on research & development on elemental technologies for all-solid-state batteries since 2001. Meanwhile, Toyota started in 2006.

This collaboration focuses on sulfide solid electrolytes, which have been a promising material for achieving high capacity and output for BEVs. Moreover, the relevant characteristics of sulfide solid electrolytes are softness and adhesiveness to other materials. For that reason, more suitable for battery mass production.

Details of Collaboration
Phase 1: Development of sulfide solid electrolytes and preparation for a large pilot facility
Both Idemitsu and Toyota will work together on creating better sulfide solid electrolytes with attention to quality, cost, and lead times. Both companies believe will realize mass-production demonstration of sulfide solid electrolytes using an Idemitsu pilot facility.
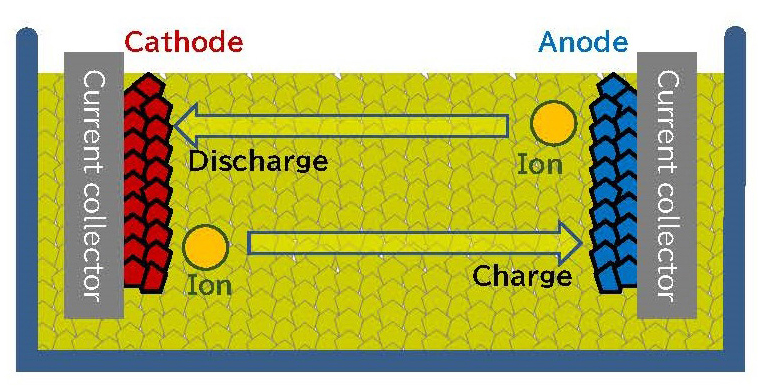
Phase 2: Mass production using a large pilot facility
Through construction and startup of a large pilot facility, Idemitsu will promote sulfide solid electrolyte manufacture. Next, it will obtain mass production technology. Meanwhile, Toyota will promote the development of both all-solid-state batteries, which will employ sulfide solid electrolytes. Next, it will also ensure the market launch of BEVs with all-solid-state batteries from 2027 to 2028.
Phase 3: Study of future full-scale mass production
Based on the results of Phase 2, both companies will study future full-scale mass production and commercialization.

Targets Global Adoption
Idemitsu has also been developing production technologies for lithium sulfide which is an intermediate material for solid electrolytes. Particularly, using by-products generated in the course of petroleum refining. Also, through such development, it has been working on the development of mass production technology on sulfide solid electrolytes. Thus, aiming to establish a stable supply system.
Furthermore, the company is steadily increasing the capacity of its small pilot facility―announced in June 2023. Next, it is proceeding construction plan of a large pilot facility announced in April 2022, which will contribute to the commercialization of all-solid-state batteries in 2027 to 2028.
Toyota and Idemitsu aim to leverage their respective strengths in material technologies to realize mass production of both solid electrolytes and all-solid-state batteries suitable for global widespread use. Moreover, both companies, working together across industries, will contribute to global carbon neutrality and will lead the future with technologies created in Japan.