ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
TANAKA Discovers New Precious Metal Recovery Process
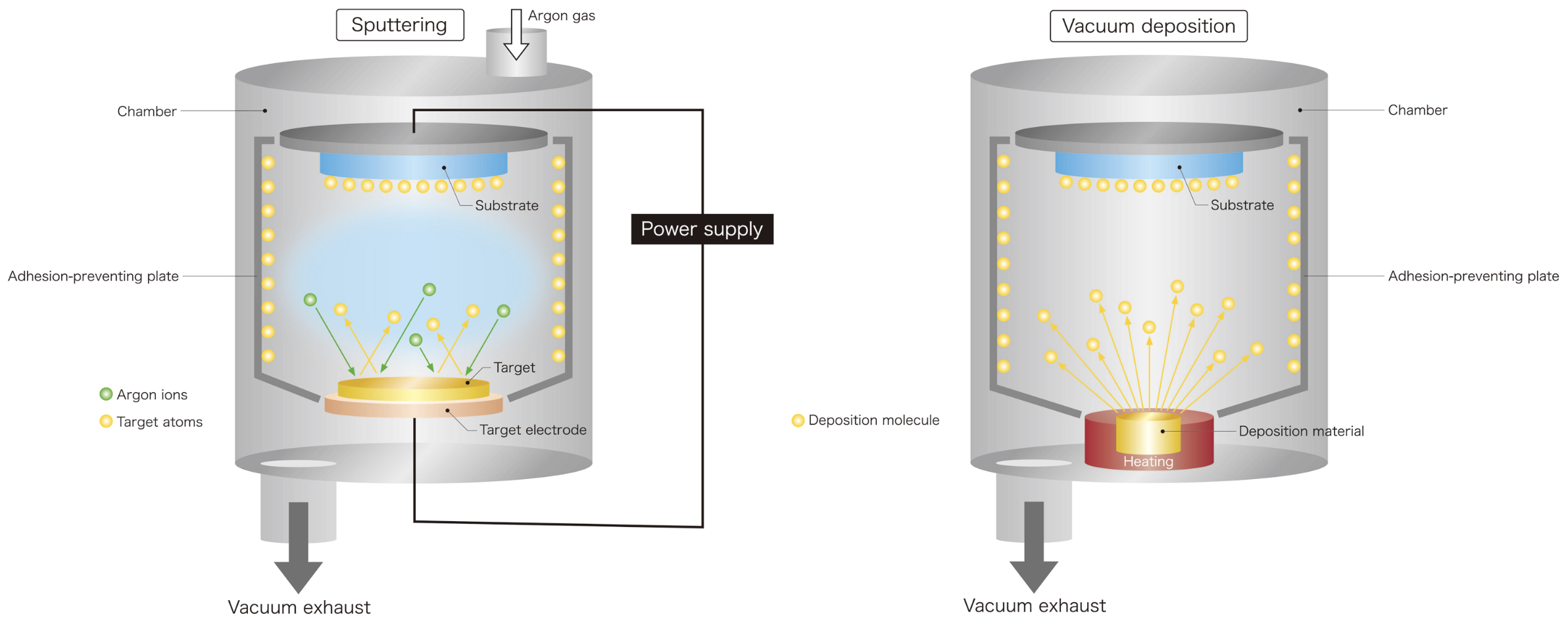
TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo K.K., which develops industrial precious metals products as one of the core companies of TANAKA Precious Metals, announced that it has established a jig cleaning method called TANAKA Green Shield. This cleaning method is characterized by nickel plating on the adhesion-preventing plate1. Specifically, it is a component of vacuum film formation equipment2 used in semiconductor manufacturing and other processes. When using a nickel-plated adhesion-preventing plate, PGM3 sputtered films, including platinum and palladium, can be easily detached from the plate.
TANAKA is developing a recycling business for this use case. The sputtered films adhering to components made from stainless steel, of vacuum film formation equipment like sputtering and vacuum deposition equipment, are detached. After that, the recovered precious metals are refined and returned to the customer with the precision-cleaned components.
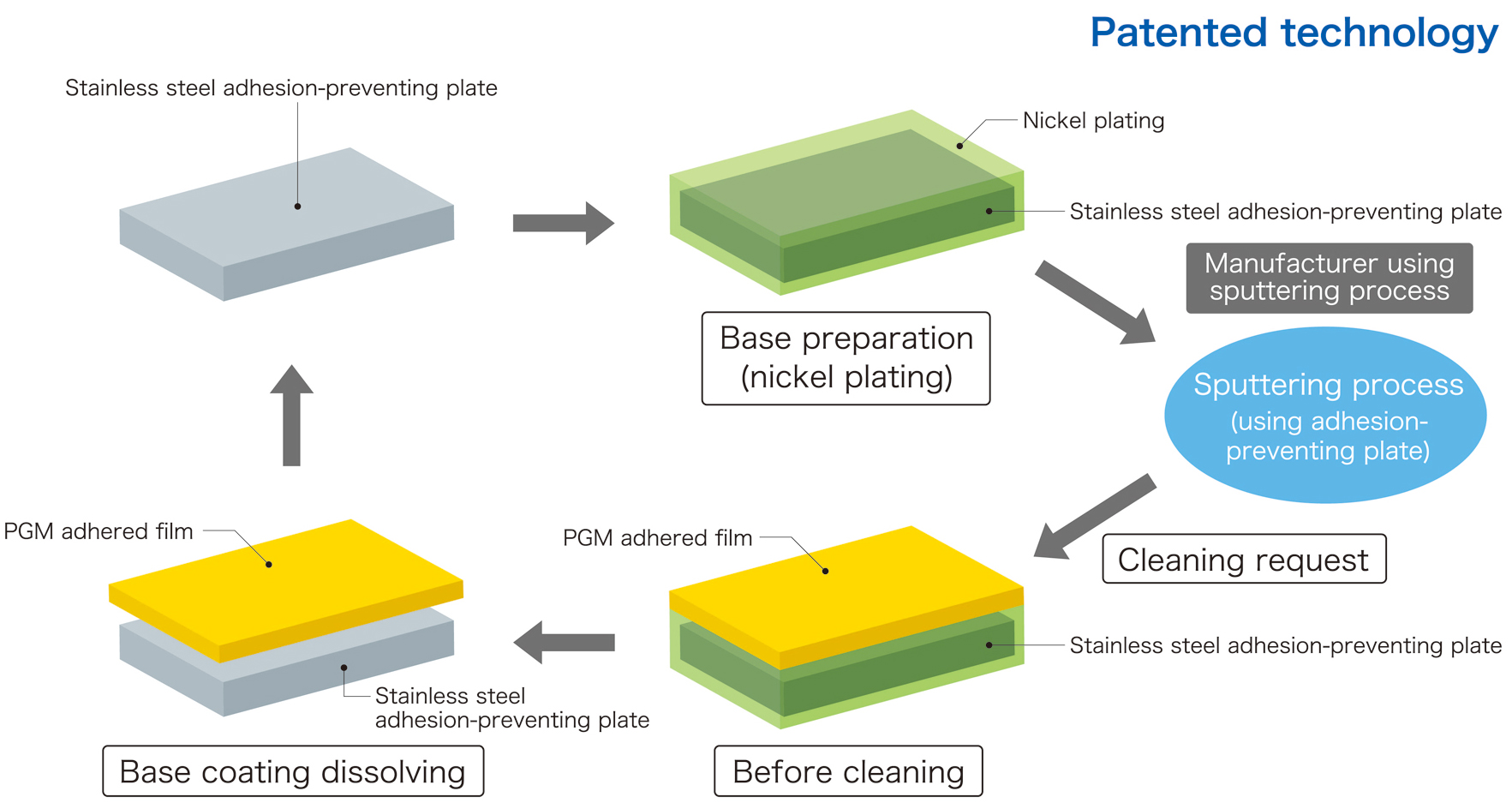
Specifically, this cleaning method takes advantage of a unique TANAKA technology related to base plating. A nickel plating is applied to an adhesion-preventing plate. It enables PGM sputtered films to be detached through chemical treatment without damaging the base material. This method makes it easier than previous methods to detach PGM sputtered films. Accordingly, it reduces the amount of cleaning agent required when cleaning equipment, in turn contributing to reduced environmental impact. A reduction in recovery loss of precious metals scattered around during the grinding process is expected. Thus, this method can achieve higher PGM recovery rates with lower costs.
TANAKA aims to develop the TANAKA Green Shield system to support a wide variety of component shapes and sizes. Also, it aims to expand PGM film recovery rates by six times the current level by 2025.
Jig Cleaning Method
Multiple jig cleaning methods for vacuum film formation equipment components are available. These include physical detachment (blast cleaning) and thermal sprayed aluminum base film formation. Mainly, physical detachment is currently a commonly used jig cleaning method due to its low cost. In physical detachment an abrasive agent (cleaning agent) is sprayed to remove an adhered film. However, the use of an abrasive agent damages the surface of the base material, leading to a shorter life. Another disadvantage of this method is that material is scattered during the process, causing a loss in precious metal recovery.
Another method for detaching an adhered film is the thermal sprayed aluminum base film formation method of jig cleaning. This requires the adhesion-preventing plate to be coated with aluminum in advance using a thermal spraying method. Also, the aluminum is dissolved with chemicals.
Drawbacks of this approach include challenges in recovering adhered film from surfaces lacking an aluminum coating, as well as the elevated cost associated with forming the aluminum film.
TANAKA Green Shield
The TANAKA Green Shield is a base preparation method whereby nickel plating is applied to an adhesion preventing plate prior to use. After using a plate in a sputtering process, for example, only the nickel plate coating between the adhesion-preventing plate and PGM sputtered film is dissolved. This enables not only the PGM sputtered film but also other adhered films with various compositions to be detached from the plate without damaging the base material. This base preparation has a high level of adhesion with adhesion-preventing plates and sputtered films, which can prevent sputtering defects caused by peeling of sputtered film.
A wide variety of component shapes can also be nickel-plated with this method. In addition to preventing degradation of the base material, this cleaning method is cheaper than the aluminum film formation method. It also requires lower amounts of cleaning agent, making it an environmentally friendly, next-generation jig cleaning method.
TANAKA and the Circular Economy
Since it was founded in 1885, TANAKA has continuously operated a precious metals recycling business. In addition to its existing precious metals recycling technologies, developed through research into precious metals over these many years, the company is now developing the TANAKA Green Shield, with a range of new precious metals recycling technologies. TANAKA’s precious metals recycling business promotes the recycling of limited precious metal resources and contributes to the realization of a circular economy.
1Adhesion-preventing plate: Plate installed to prevent film adhering to the interior wall of a film formation chamber (sealed reaction vessel used for producing physical or chemical reactions)
2Vacuum film formation equipment: Equipment used in thin film formation processes, including sputtering and deposition, employed in the manufacture of semiconductors
3PGM: Platinum group metals comprising six precious metals (platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium, and osmium)




