ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
Murata's Reliable Material to Cut More on Metal Need
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. has introduced a revolutionary ceramic catalyst material designed to reduce industrial gas exhaust systems.
Accordingly, a Chinese manufacturer Shanghai FT Technology Co., Ltd, makes and sells ceramic catalysts using this material. Unlike traditional catalysts in exhaust treatment systems, this ceramic solution does not contain any precious metals. Moreover, it significantly reduces both the consumption of the natural gas used for treatment and CO2 emissions.
Across industrial production processes, exhaust gasses need treatment to prevent harmful particulate matter from entering the atmosphere. Nonetheless, in many applications, regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTO) are necessary. Particularly, to decompose and treat the exhaust gas by burning it with natural gas. Therefore, eliminating volatile organic compounds (VOCs), hazardous air pollutants (HAPs), and odorous emissions produced during industrial processes.

Reduce Natural Gas Use
Globally, prices of natural gas continue to increase and so is the urgent need to prioritize global sustainability. For that reason, industrial production facilities are finding ways to decrease fuel consumption and reduce carbon footprint.
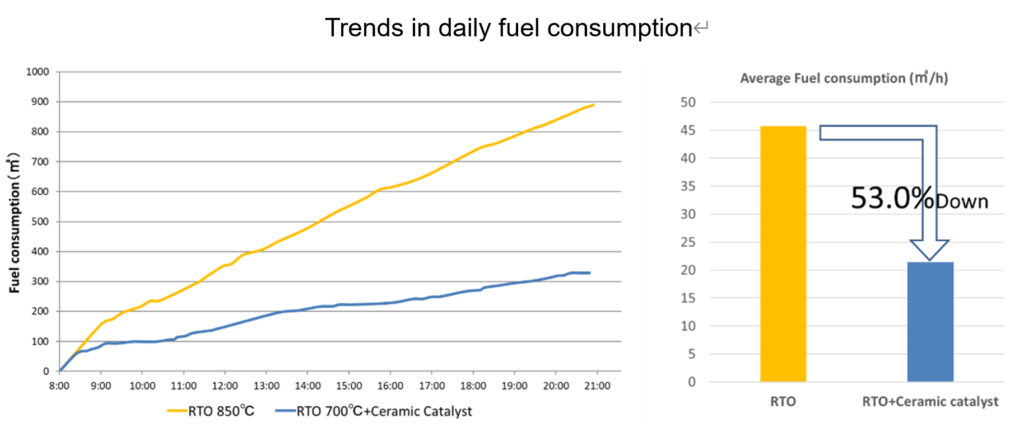
Built from Murata’s extensive ceramic capacitor knowledge, the catalyst exhibits exceptional heat resistance and can treat highly concentrated exhaust gas. In terms of performance, Murata’s ceramic catalyst can lower the temperature of an existing exhaust gas treatment equipment to around 850℃ to 700℃. Thus, reducing the set temperature system can translate to reduced heat loss and increased self-combustion rate. Thereby, reducing natural gas consumption by up to 53% (Figure 1).
In addition, this change in operational conditions results in a decrease in CO2 emissions originating from natural gas usage. Therefore, contributing to a decrease in environmental impact, as well as significantly lowering running costs.
Creates Innovative Solution
The ceramic material also brings several advantages. Primarily, the initial system cost is far more predictable, free from the price fluctuations seen with precious metals. Furthermore, the performance of precious metal catalysts can become compromised when subjected to extremely high temperatures, as the active element can move and group into larger clusters. This process, referred to as sintering, reduces the number and area of active sites and deteriorates the catalyst’s performance. Alternatively, ceramic catalyst materials have active elements dispersed in their crystal structure and do not degrade even in high-temperature operation. Thus, leading to an extended lifespan compared to precious metal catalysts.
In real-world applications at both Murata’s manufacturing and partner sites, the ceramic catalyst has had a significant impact on the environmental impact of RTO systems and operating costs. Particularly, with the installation at Wuxi Murata Electronics Co. achieving full system payback in just 13 months.
“With Murata’s patented ceramic catalyst material, we have taken our extensive ceramic capacitor knowledge and applied it to another market to create a truly innovative solution,” said Koichi Kawakita, Vice President Manufacturing Group Ceramic Capacitor Business Unit.
In addition, Kawakita said, “In terms of operation, it can help factory designers and exhaust gas treatment manufacturers achieve significant reductions in natural gas consumption and carbon emissions. While also cutting dependence on precious metals.”
-12 April 2024-




