ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
Smart Factory Reinvents Supply Chain Strategy
With the spread of internet of things (IoT), smart factory has been attracting attention as one application that will make use of this emerging technology.
Moreover, smart factory realizes mass customization that meets demands. In mass customization, digital twin plays key role in real-time production management. In addition, digital twin merges cyber space and real space and simulate use-case conditions.
Thus, smart manufacturing will bring changes to new business models using mass customization and will innovate further the manufacturing processes.
IoT Revs up Supply Chain System
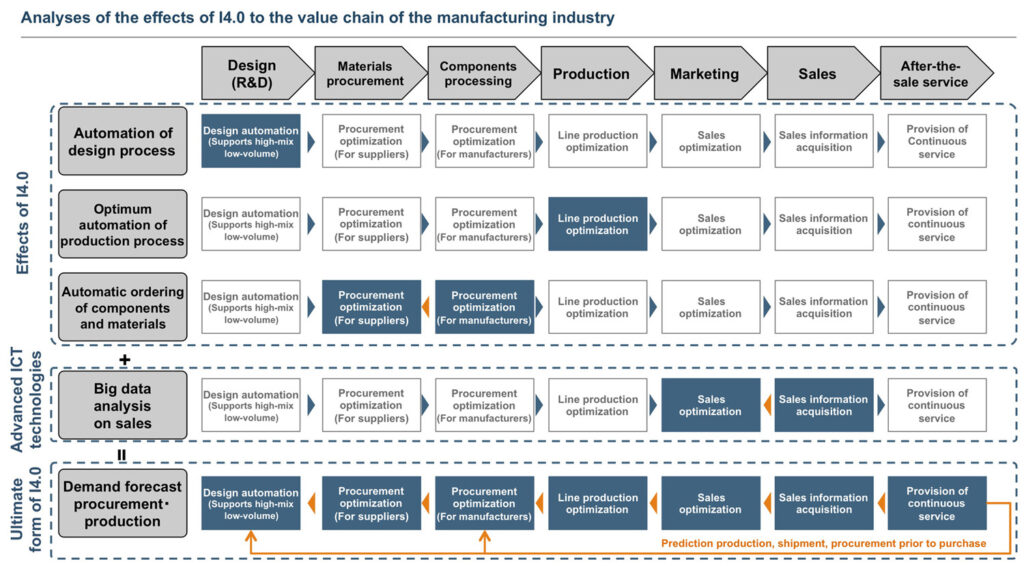
IoT technology in manufacturing has brought major changes to supply chains through Industry 4.0. That is, the fusion through IoT technology, has paved the way to pull-type manufacturing in accordance with demand. As such, this brought the shift from push-type manufacturing to manufacture products assuming demand. Thus, the IoT technology has brought about the backward flow in the value chain.
Mass customization provides necessary specifications and quantities. They enable manufacturers to break away from the conventional business based on mass production. Thus, it allows the new business models through linkage with other innovations, such as demand prediction with higher accuracy and logistics reform, using IoT technology.
Smart Factory Tackles Mass Production Head on
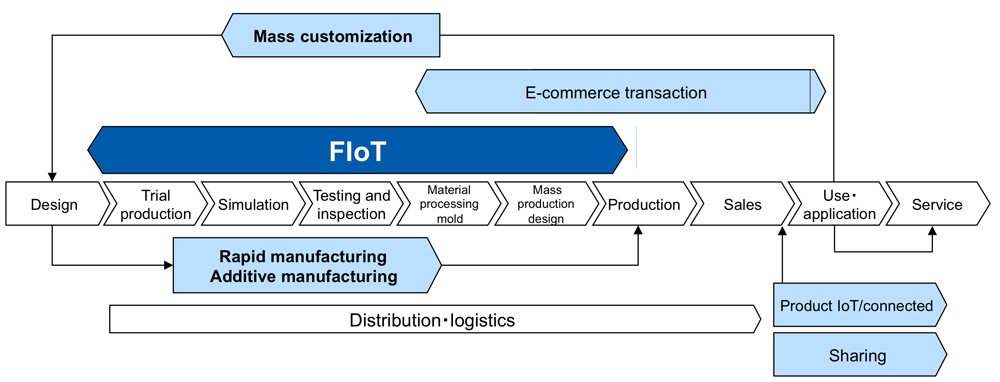
Meanwhile, IoT technology has paved the way to new business models, including subscription-based smart manufacturing business. To illustrate, this business model provides necessary conditions to promote effective mass customization using smart manufacturing.
Diverse components produced by mass production can create a similar mechanism to cope with changes of business. However, such method is not good enough to compete with businesses based on factories, such as electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies. Companies that are set to make investments for new business as new manufacturing should carry out mass customization in smart factory.
To this end, it is necessary to construct a new manufacturing instead of the business on the assumption of manufacturing. It is necessary to optimize manufacturing in accordance with any conditions, e-commerce transactions, and logistics, based on the analyses of customers’ use conditions (such as sharing of subscriptions).
To achieve such system, it is necessary to focus on the countries that will strengthen manufacturing. At the same time, it is necessary to include emerging countries rather than countries that already have legacy, production system, and supply chain.
Importance of Smart Factory in Southeast Asia
Accordingly, China is strong in manufacturing and India is strong in information technology. These countries focus on the improvement of mass production efficiency targeting large demand locations. Legacy business assets tend to sway these countries, hence making it difficult to achieve smart factory, including reform in business structure.
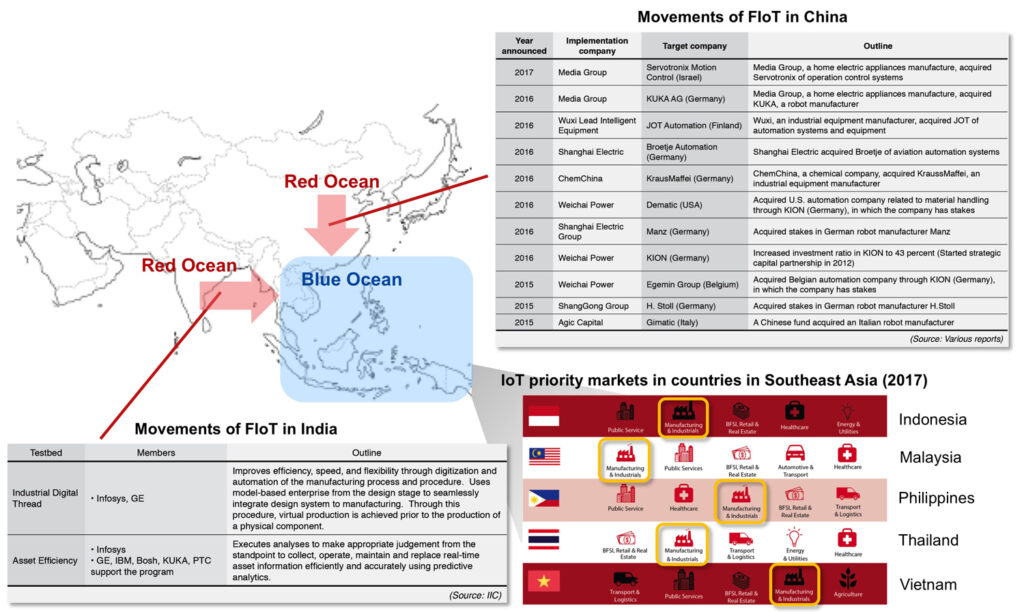
In addition, many companies in these markets, including not only domestic manufacturers but also foreign companies, have entered the smart factory market. They look already read ocean markets.
In contrast, countries in Southeast Asia, where the shift of manufacturing from China, their governments have set forth policies to strengthen manufacturing. These markets may construct smart factory that brings about fundamental business reforms by incorporating new technologies.
About This Article:
The author is Kenichi Sasaki, Senior Consultant, Consulting Department, Nomura Research Institute, Ltd.