ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
Toshiba Enables Smooth Collision Avoidance of Robots
Toshiba Corporation has developed a cooperation and coordination system where a multitude of autonomous mobile robots directly communicate and work collaboratively with each other. Because of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, the need to reduce contact among people also increased and so as the need for robots that enable smooth collision avoidance.
Because of use, the use of robots and automation has been gaining traction in manufacturing facilities and other environments.
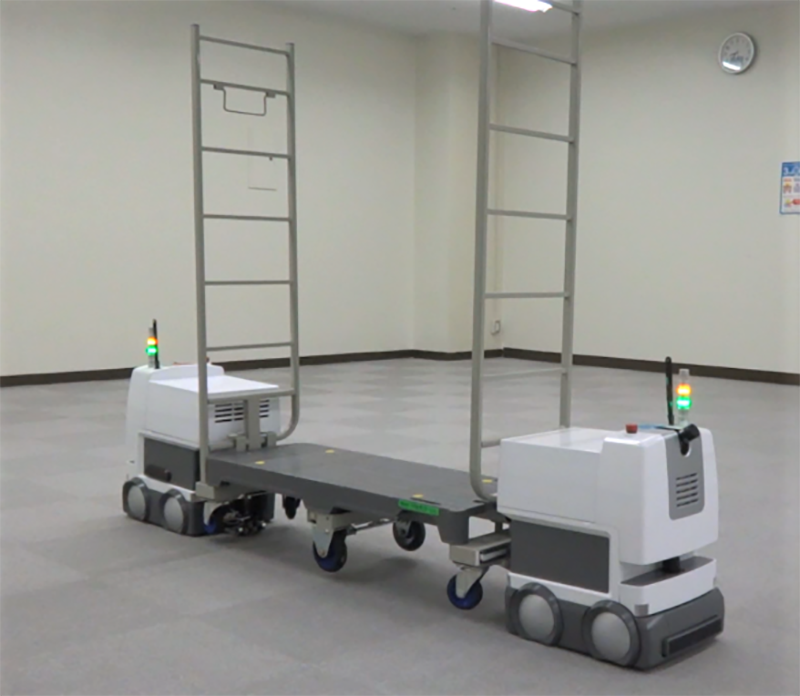

Confirms Smooth Collision Avoidance
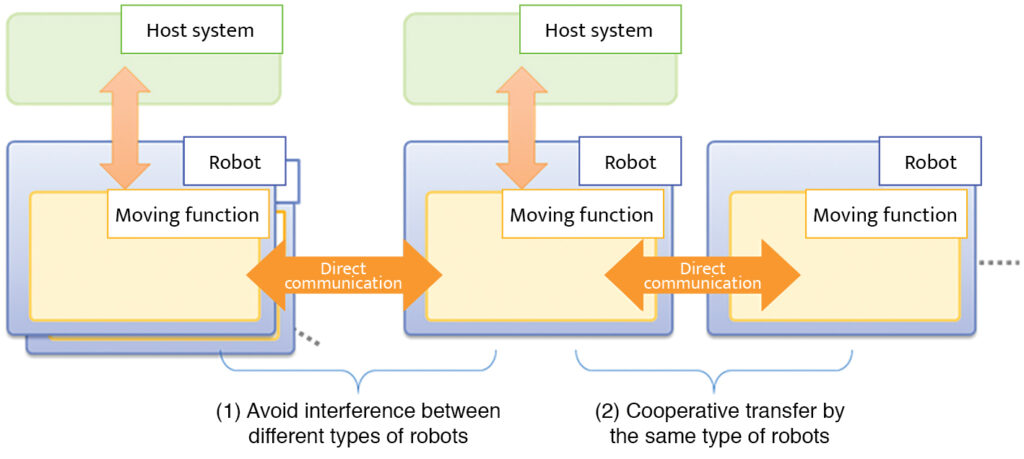
The system Toshiba developed features direct communications among robots without using an operating system. It adopts multihop wireless local area network system, which transmits data in a bucket brigade manner. This enables robots to exchange information with one another in real time. Toshiba targets practical use of the system eyeing application in stations, commercial facilities, and office buildings.
Existing robots can avoid collision to obstacles that are at a stop. However, when robots are moving, they cannot recognize each other’s travel direction and avoiding collision is difficult.
Toshiba conducted demonstration experiments of the coordination of robots in collaboration with Shibaura Institute of Technology.
The demonstration experiments confirmed smooth collision avoidance between robots by sharing each other’s position and travel direction. The company has enabled even robots with different operation systems to avoid collision.
Accommodates Robots of Same Kind
Toshiba also confirmed that a plurality of the same type of robots can transfer an object while matching the timing. By adding robots, the system can accommodate objects of various sizes and weights.
Autonomous mobile robots are attracting attention to solve labor shortages as they can substitute tasks with large workloads. Applications of robots have been expanding.
When using robots for transfer in manufacturing and logistics sites, in general, it is more manageable to use of plurality of robots of the same model and of the same manufacturer. On the other hand, some public facilities employ robots from different manufacturers for different applications.
As different manufacturers create original operating systems, most robots will not be able to share position and other relevant information for smoother collision avoidance.