ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
China’s Domestic Firms to Propel Industrial Robot Market
While the manufacturing industry in China is continuously faced with the challenges of labor saving and automation, the country is set to create a huge industrial market that can be considered largest in the world.
Previously, the sales ratio of overseas manufacturers in China’s industrial market was high, but in recent years, domestic production by Chinese manufacturers has been increasing on back of the promotion of “Made in China 2025”.
Characteristics of China’s Robots Market
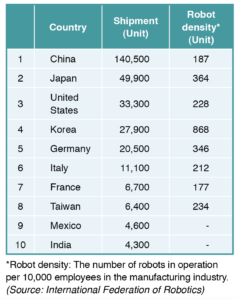
According to International Federation of Robotics (IFR), global sales of robots (main bodies) in 2019 decreased 12 percent from the previous year to 373,000 units. By region, sales in China accounted for about 40 percent at 140,500 units; still maintaining a high level despite a decrease of 9 percent from the previous year.
According to IFR, China’s robot density, which is the number of industrial robots used per 10,000 employees, is ranked 15th globally with 187 units or half with that of Japan with 364 units. This indicates the installation of robots in China will accelerate in the coming years.

Main applications of industrial robots in China include assembly and transfer (SCARA robots and compact vertical articulated robots for the production of smartphones, and electronic devices), welding and painting [mainly in automobiles and electric vehicles (EVs) production line], clean transfer (transfer of flat panel displays and wafers), and actuators (single-axis robots, and orthogonal robots).
Sales of robots (main bodies) in China by overseas manufacturers still remained high in 2019, accounting for 71 percent. Japanese manufacturers, including Yaskawa Electric Corporation, FANUC Corporation, NACHI-FUJIKOSHI CORP., Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd., Seiko Epson Corp., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, DENSO Corporation, and Panasonic Corporation, as well as AGG Group of Switzerland, Universal Robots A/S of Denmark, KUKA AG of Germany, HIWIN Technologies Corp. of Taiwan, and Hyundai of Korea compete in the Chinese market.
Domestic Robot Makers
Meanwhile, the rise of Chinese manufacturers has been remarkable. They have been catching up with Japanese makers in the manufacture of articulated robots with six or more axes, which are considered technically difficult. “Made in China 2025” positions the robot industry (machine tools) as one of the 10 priority fields, and the country has been promoting domestic production of industrial robots as a state policy. Chinese manufacturers’ share of the domestic market increased from 22 percent in 2017, 29 percent in 2019, and is estimated to have reached the 30 percent level in 2020.
State-run SIASUN Robot & Automation, the largest robot manufacturer in China, based in Shenyang in Liaoning Province, is a high-tech listed company, which belongs to Chinese Academy of Sciences, China’s top-level science and technology organization. It has its main plant in Shenyang. The company manufactures collaborative robots as well and exhibited its products at SEMICON China 2021 held in Shanghai in March. Nanjing Panda Electronics Co., Ltd. based in Nanjing, Jiangsu Province is almost equal in size to the SIASUN Group, except that it adopts Japanese-made components in the drive section of robots.

Standard Robots Co., Ltd. in Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, specializes in research and development and manufacture of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs). The company takes part in exhibitions of distribution equipment in Japan as well. Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) positioning, beacon positioning, inertial navigation and other technologies the company has developed in-house are high levels in terms of international standards. The company has a track record of delivering its products to many large companies, such as Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., ZTE Corp., Foxconn, and Volkswagen.
Midea Group, a leading Chinese manufacturer of home electric appliances, acquired KUKA in 2016 following the acquisition of Toshiba Corp.’s white goods business in the same year. ForwardX Robotics, Inc. in Beijing, manufactures collaborative AMRs. Aside from the above-described manufacturers, Estun Automation Co., Ltd. in Nanjing, Guangdong Topstar Technology Co., Ltd. in Dongguan, Guangdong Province, and Shanghai STEP Electric Corporation in Shanghai play their part in the Chinese robot industry as leading companies.
Double-Digit Increase in Production
Although IFR has not yet announced the global sales in 2020, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has recently announced that the production of industrial robots in China in 2020 increased 19.1 percent from the previous year to 237,068 units.
According to robot statistics by the Japan Robot Association (JARA), total shipment in 2020 rose for the first time in two years by 1.9 percent from the previous year to 179,074 units. China, which has recovered from the novel coronavirus pandemic, drove the increase. In January to March quarter in 2021, both the received orders and production value were record high for a quarter. Shipments to China were ¥84 billion, accounting for 51 percent of total exports from Japan, significantly exceeding ¥68.1 billion in July to September quarter in 2017, which was the record high. The Chinese robot market continues to expand.