ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
Manufacturing Sites Gain More From High Accuracy AI
Toshiba Corporation has developed an accurate and highly versatile Visual Question Answering (VQA) artificial intelligence (AI). The system can recognize not only people and objects, but also colors, shapes, appearances, and background details.
The AI overcomes the long-standing difficulty of answering questions on the appearance of people and objects and other relevant questions. The system suits wide range of applications without further modification.
In experiments using a public dataset1 comprising a large volume of images and data text, the VQA AI correctly answered 66.25 percent of questions without any pre-learning and 74.57 percent with pre-learning. For example, the AI can find a worker standing in a designated place by asking questions like, “Is the person on a black rug?”. This requires recognition of the individual, position, shape, and color. Applying it to safety monitoring systems at production sites can help improve safety and reduce workloads of onsite supervisors. It can also identify specific scenes in broadcast content and surveillance video footage.
Toshiba presented on September 14 the technology at ICANN20212, the international conference for neural networks.
Potentials of AI
In the coming years, Japan expects to experience growing problem on manpower shortages in manufacturing facilities. This has been also apparent in other advanced countries. The onset of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic even made the situation worse as workers safety takes primordial concern.
Manufacturers has been eyeing the use of AI in production sites as a solution to growing labor challenges. Analysts forecasted the global AI market, including software, hardware, and services, to grow 16.4 percent in 2021 year-on-year to reach US$554.3 billion in 20243.

Current image recognition AI supports safety inspections at the level where it can detect individual objects learned beforehand, such as people, headwear, and work clothing. This analyzes camera images and determine whether someone is wearing a hardhat, or to detect dropped or fallen objects, helping to ensure workplace safety and reduce the site management workload.
However, getting to this point requires the creation of a determination function that will help AI recognize an inspection item. For example, when checking for headgear, it must learn how to detect and determine if an individual is wearing a hat, hence the system must detect everyone first. However, this is difficult with the current AI set up and determination function as changes in inspection items may happen from time to time.

Extends Features of Conventional AI
Toshiba’s new AI is highly flexible and accurate and can change or add questions and other parameters quickly. It can recognize not only people and objects but also image backgrounds. It also offers an extensive database at its disposal, ensure that it can quickly process the features of images and pre-learned questions to derive the correct answer. After learning a large set of images, questions and answers that cover the presence of people and objects, and information such as their location and status, the AI can provide an appropriate answer to a question from 3,000 answer patterns.
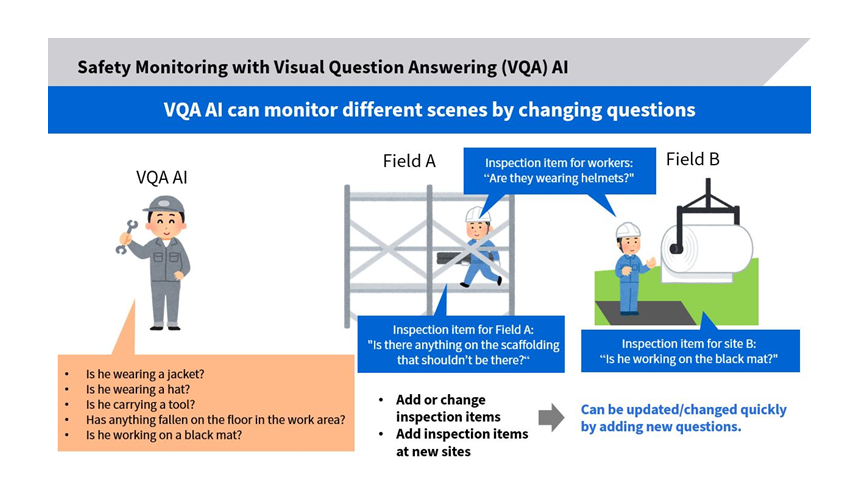
The AI is highly flexible to new inspection items, or changed to handle a different situation, by a simple “Image and Question” process of adding new question sentences (Fig. 1).
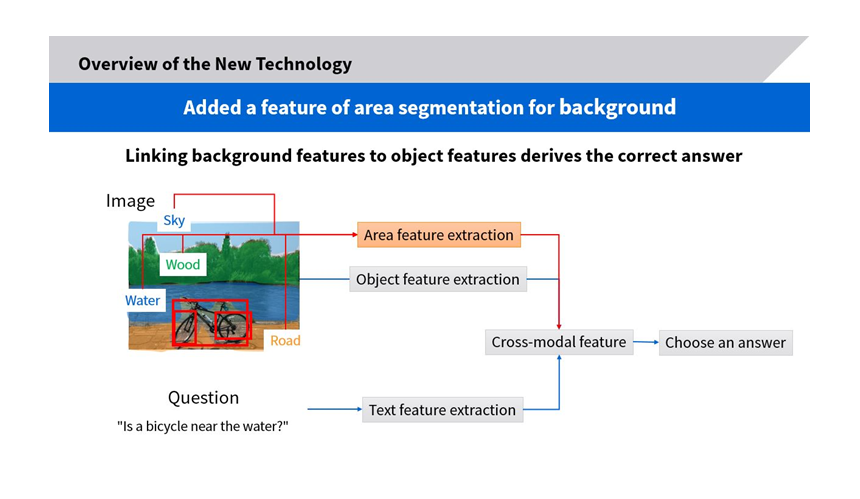
AI for VQA is a cutting edge-technology researchers around the world are investigating. The conventional approach4 relies on the features of people and objects in an image, but Toshiba’s new method also extracts background features and spatial areas, including the floors and passageways where these people and objects may be present (Fig. 2). This feature enables the new AI to derive accurate answers.
For example, the AI can answer questions such as whether there is an object on a path. It can also check if a person is standing in a designated area, or the presence of an object (Fig 3 and 4). Applying this AI to safety monitoring at production sites will improve workplace safety, reduce workloads on supervisors, and contribute to work style improvement.
Suits Wide Range of Application
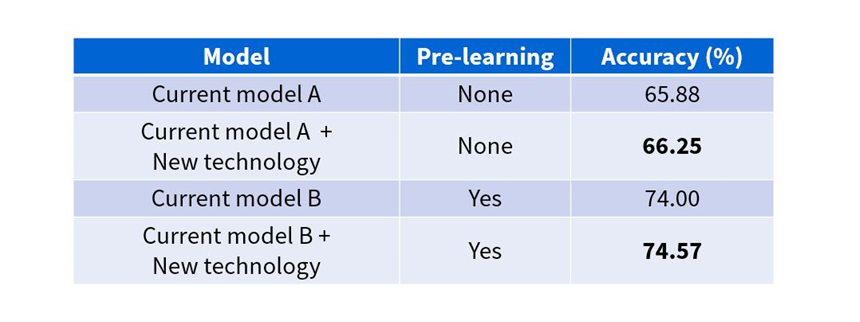
In a performance evaluation with a global standard public dataset, Toshiba achieved accuracy levels of 66.25 percent without pre-learning and 74.57 percent with pre-learning, the highest levels ever recorded5. Results with the current methods showed accuracy of only 65.88 percent without pre-learning and 74 percent with pre-learning (Fig. 5).
The versatility of the new AI suits wide range of applications, such as searching for specific scenes from broadcast contents or specific circumstances. It can also look for people in a disc drive recorders and security footages and other similar scenarios.
Toshiba will continue system development and accuracy improvement, toward introducing the AI technology into safety monitoring systems in 2023.
Notes:
1 VQA-v2 data set Antol, S., Agrawal, A., Lu, J., Mitchell, M., Batra, D., Zitnick, C.L., Parikh, D.: VQA: Visual Question Answering. In: ICCV (2015)
2 The 30th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks held online from September 14th to 17th.
3 Source: IDC Forecasts Improved Growth for Global AI Market in 2021
4 Li, Linjie and Gan, Zhe and Cheng, Yu and Liu, Jingjing: Relation-aware Graph Attention Network for Visual Question Answering: ICCV (2019)
5 As of the paper submission date (April 15, 2021)
6 Image source: Okayama Labor Bureau, Ministry of Health (Japanese)
7 Image source: Labour and Welfare, Ministry of Health (Japanese)




