ASIA ELECTRONICS INDUSTRYYOUR WINDOW TO SMART MANUFACTURING
Makers Boost 300MM Capacity as Power ICs Gather Steam
Investments to boost production of power semiconductors, which control and supply power, have been gathering momentum. Particularly, amid robust demand, the transition to manufacturing lines that support 300mm wafers has been advancing. Hence, efficiently expanding production capacities.
Following European and U.S. manufacturers, Japanese companies have also been accelerating investments to install manufacturing lines for 300mm wafers. Competition for market share will likely intensify.
Meanwhile, Fuji Keizai Co., Ltd., the global power semiconductor market in 2021, grew 20.7 percent year-on-year. At the back of the growth was the expansion in demand for power semiconductors in a wide range of fields. This includes consumer equipment, industrial, and information and communications equipment. Most importantly, the growth happened at the time of rapid advancement of digitalization and the onslaught of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Fuji Keizai forecasts that the market in 2022 will sustain expansion, increasing 11.8 percent annually. However, the growth will slow somehow amid the shortages of components.
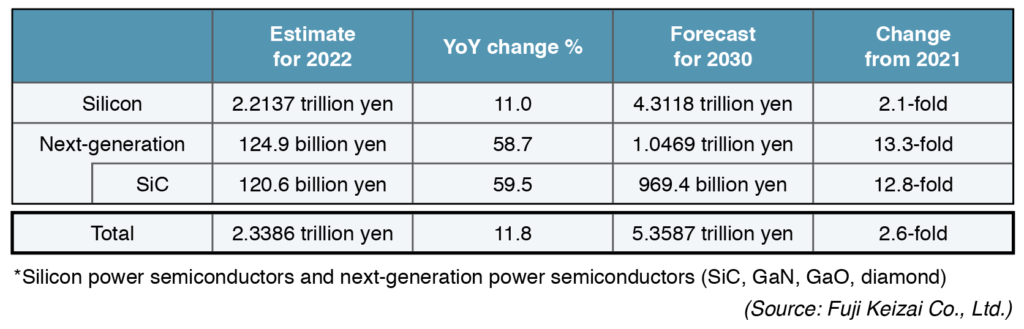
Furthermore, as major countries are steering toward decarbonization, vehicle electrification and widespread use of renewable energy will make progress. Equally important, these trends as tailwind will push global power semiconductor to reach ¥5.36 trillion (US$39.35 billion) in 2030. This, Fuji Keizai said, will comprise 2.6-fold increase from 2021.
Reinforce 300mm Fab Capacities
Germany-based Infineon Technologies AG started operation of a new plant in Villach, Austria in August 2021. Specifically, the Villach Plant is the company’s second 300mm wafer fab, next to Dresden in Germany. The company invested €1.6 billion (US$1.68 billion), which is one of the largest investments made by a semiconductor company in Europe.

Particularly, the plants manufacture power semiconductors notably for electric vehicles (EVs) and data centers. In addition, they also target photovoltaic and wind power generation systems. Infineon plans to expand production capacity of the plants in four to five years in stages to capture demand. The company expects the Villach plant to churn annual sales of €2 billion once full operation. The company intends to pull ahead of competitors in one go.
Originally, high-mix, low-volume production was required for power semiconductors, and therefore, manufacture in 200mm lines has been the mainstream. However, with significant expansion of the market, increasing number of companies are promoting the transition to 300mm wafers anticipating efficient production increase and improved performance. They also expect the smartification of factories by installing standardized equipment.
On the other hand, number two semiconductor company ON Semiconductor Corporation acquired in 2019 from GLOBALFOUNDRIES a 300mm fab. Located in East Fishkill, New York, the ON Semiconductor purchase costed US$430 million. Particularly, ON Semiconductor plans to start mass producing power semiconductors for automobiles at the fab.
Meanwhile, STMicroelectronics has completed a 300mm fab at its Agrate Brianza site in the suburbs of Milan, Italy. Moreover, the company plans to start producing power semiconductors, analog mixed signal integrated circuits, and other products in the second half of 2022.
Japan Makers Show Force, Too
With new fab expansions Infineon, ON Semiconductor, and STMicroelectronics have jumpstarted, many companies are following suit. For example, Japanese companies are also joining the foray to construct 300mm wafers.
First, Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corporation (Toshiba) (Kanagawa Prefecture) announced last year of its plan to install a 300mm wafer fabrication facility at its existing manufacturing factory building at Kaga Toshiba Electronics Corporation (Ishikawa Prefecture), its production subsidiary in Japan. The company will start mass production on the new line in the second half of FY2022. Somehow, this brought forward the company’s initial plan.
Earlier in February, Toshiba announced that it planned to invest ¥100 billion to construct a power semiconductor manufacturing factory building on the premises of Kaga Toshiba Electronics. Particularly, this will support 300mm wafers as well.
Toshiba plans to proceed with the construction in two phases, while watching the market trend. In the first phase, the company plans to start operations by the end of FY2024 to manufacture low-voltage metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). In addition, it will also manufacture insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs), which are indispensable for EV inverters, as well as other devices. Hence, this will boost its production capacity for power semiconductors to 2.5-fold of FY2021.
Other Technologies Pull Through
Renesas Electronics Corporation plans to reopen its Kofu Plant it once closed in 2024 as a 300mm wafer fab capable of manufacturing power semiconductors. The company will invest ¥90 billion in the fab. Here, Renesas plans to produce IGBTs for automobiles and other devices, thereby doubling its production capacity for power semiconductors.
Meanwhile, DENSO Corporation will collaborate with United Semiconductor Japan Co., Ltd. (USJC), a subsidiary of leading Taiwanese semiconductor foundry United Microelectronics Corporation (UMC). The companies will construct a 300mm wafer fabrication line at USJC’s Mie Plant (Kuwana, Mie Prefecture). Mass production of IGBTs scheduled to start in the first half of 2023.
Finally, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, the largest power semiconductor manufacturer in Japan, started in spring production of power semiconductors at Fukuyama Works the company acquired from Sharp Corporation. The company plans to put to operation a 300mm line at the plant in FY2024.
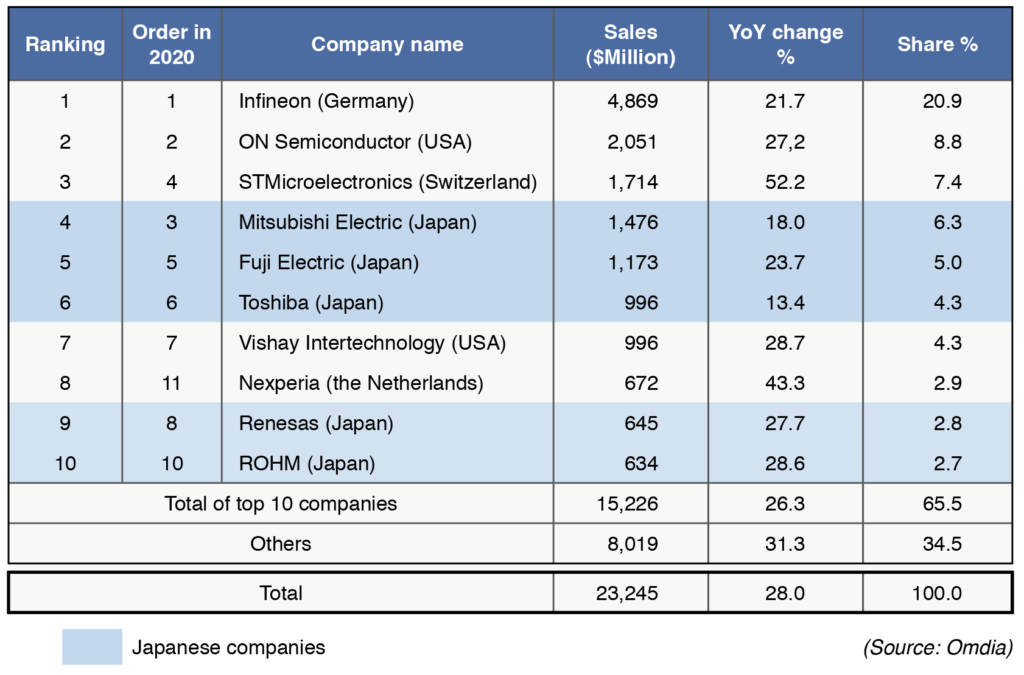
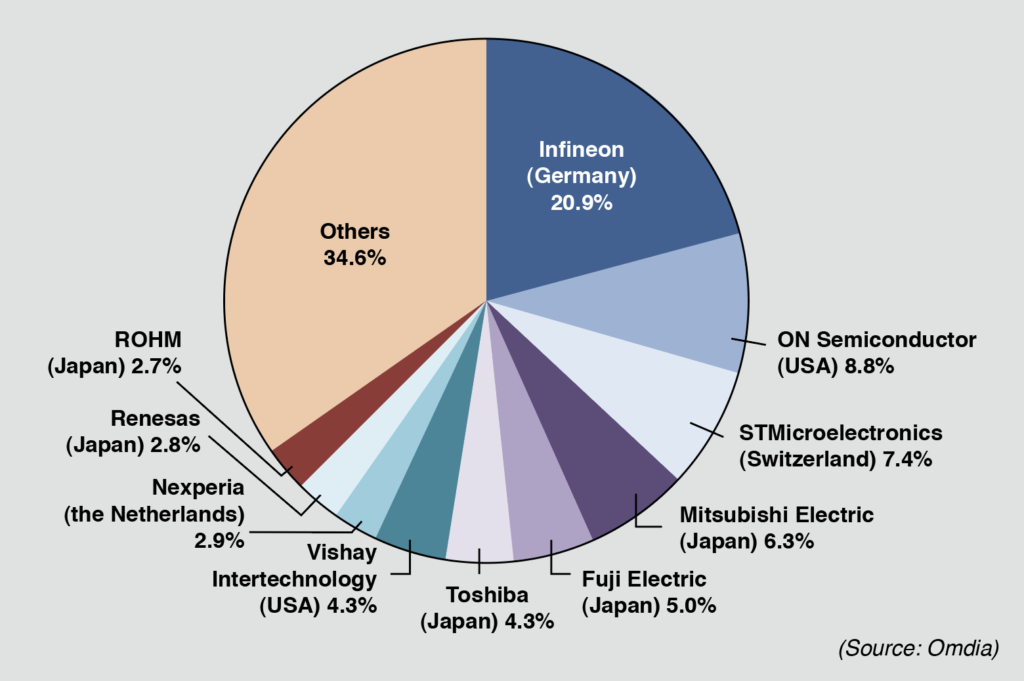
Power semiconductors have been the core strength of Japanese manufacturers. British research firm Omdia said global ranking in 2021 showed European and U.S. companies occupying the top three spots. However, five Japanese companies managed to enter the top 10. Aside from the installation of 300mm wafer fabrication facilities, Fuji Electric and ROHM have been going on an offensive by boosting the production of next-generation power semiconductors using silicon carbide (SiC), a trump card for energy saving. Moreover, they are targeting to be among the top spots globally.
Recently, Chinese companies have been catching up at a remarkable pace, and market competition will likely intensify. Nonetheless, Japanese companies will invest boldly to build momentum to increase their market shares.




